Convolutional Operator Learning for Imaging
Data-driven and learning-based approaches have gained much interest in recent years for medical image reconstruction. These methods learn representations of images and are used in combination with model-based techniques to perform complex mappings between corrupted measurements and high-quality images.
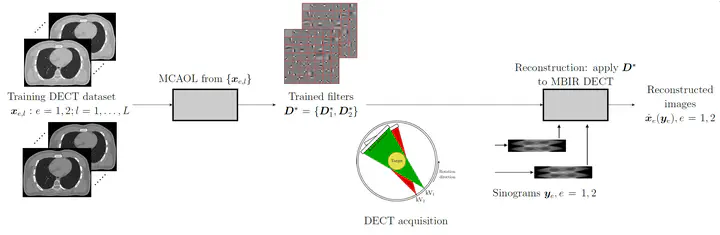
In this project, we develop a multi-channel convolutional analysis operator learning (MCAOL) framework that can exploit direct joint reconstruction, given the low-dose DECT measurements, where all the unknown images are reconstructed simultaneously by solving one combined optimization problem.
MCAOL requires considerably less memory compared to alternative DL approaches. The joint reconstruction approach is developed for a low-dose data acquisition protocol which consists of collecting data using a sparse angular sampling, using a different X-ray energy in consecutive steps and low X-ray photon counts. In Dual Energy CT (DECT), a reasonable prior assumption is that attenuation images at different energies can be expected to be structurally similar in the sense that an edge (e.g., an organ boundary) that is present at one energy, is likely to be at same location and alignment with the other energies as well, even though the contrast between materials will be different at each energy.
MCAOL technique reconstructs attenuation images from the projection data combined with multi-channel filters trained on a dataset of reconstructed images. The central idea of MCAOL is to learn unsupervised DECT muti-channel convolutional dictionaries that can provide a joint sparse representation of the underlined images by jointly learning filters for the different energies: each atom not only carries individual information for each energy individually but also inter-energy information. By reconstructing DECT images using MBIR techniques in conjunction with MCAOL, the multi-energy information can be optimally used by allowing the images to “talk to each other” during the reconstruction process through the learned joint dictionaries, reducing noise while preserving image resolution.